4 Setting up the Greenbone Enterprise Appliance¶
4.1 Setup Requirements¶
4.1.1 Greenbone Enterprise 6500/5400¶
The Greenbone Enterprise 5400 and Greenbone Enterprise 6500 are 19-inch mountable and require two rack units (RU). Rack holders for the installation in a 19-inch rack are supplied.
For cabling, the Greenbone Enterprise 5400 and Greenbone Enterprise 6500 have corresponding connectors at the front and back:
- Front
1 RJ45 console port, suitable cable is enclosed
1 Mini-USB console port
2 USB 3.0 ports
2 RJ45 Ethernet ports, labeled “MGMT”, for management
1 module with 8 RJ45 Ethernet ports
Note
Additional network modules must be purchased separately. A maximum of 4 network modules can be installed in total. The network modules can contain either up to 8 RJ45, 8 SFP or 2 SFP+ Ethernet ports.
- Back
1 VGA port
1 USB 2.0 port
2 power supplies
The installation requires either a monitor and a keyboard or a serial console connection and a terminal application.
4.1.2 Greenbone Enterprise 650/600/450/400¶
The Greenbone Enterprise 400, Greenbone Enterprise 450, Greenbone Enterprise 600 and Greenbone Enterprise 650 are 19-inch mountable and require one rack unit (RU). Rack holders for the installation in a 19-inch rack are supplied.
For cabling, the Greenbone Enterprise 400, Greenbone Enterprise 450, Greenbone Enterprise 600 and Greenbone Enterprise 650 have corresponding connectors at the front and back:
- Front
1 RJ45 console port, suitable cable is enclosed
2 USB 3.0 ports
8 RJ45 Ethernet ports
2 SFP Ethernet ports
- Back
1 VGA port
1 power supply
The installation requires either a monitor and a keyboard or a serial console connection and a terminal application.
4.1.3 Greenbone Enterprise 150¶
The Greenbone Enterprise 150 is 19-inch mountable and requires one rack unit (RU). The optional RACKMOUNT150 kit provides the rack holders for installing the appliance in a 19-inch rack.
For stand-alone appliances, four self-sticking rubber pads have to be mounted on the corresponding bottom side embossments.
For cabling, the Greenbone Enterprise 150 has corresponding connectors at the front and back:
- Front
1 RJ45 console port, suitable cable is enclosed
2 USB 3.0 ports
1 HDMI port
4 RJ45 Ethernet ports
- Back
1 power supply
The installation requires either a monitor and a keyboard or a serial console connection and a terminal application.
4.1.4 Greenbone Enterprise 35¶
The Greenbone Enterprise 35 is 19-inch mountable and requires one rack unit (RU). The optional RACKMOUNT35 kit provides the rack holders for installing the appliance in a 19-inch rack.
For stand-alone appliances, four self-sticking rubber pads have to be mounted on the corresponding bottom side embossments.
For cabling, the Greenbone Enterprise 35 has corresponding connectors at the front and back:
- Front
1 RJ45 console port, suitable cable is enclosed
2 USB 3.0 ports
1 HDMI port
4 RJ45 Ethernet ports
- Back
1 power supply
The installation requires either a monitor and a keyboard or a serial console connection and a terminal application.
4.1.5 Greenbone Enterprise DECA/TERA/PETA/EXA¶
This section lists the requirements for successfully deploying a Greenbone Enterprise DECA, Greenbone Enterprise TERA, Greenbone Enterprise PETA or Greenbone Enterprise EXA. All requirements have to be met.
The virtual appliances require and are limited to the following resources:
Greenbone Enterprise DECA
4 virtual CPUs
14 GB RAM
500 GB virtual hard disk
Greenbone Enterprise TERA
6 virtual CPUs
14 GB RAM
500 GB virtual hard disk
Greenbone Enterprise PETA
8 virtual CPUs
16 GB RAM
500 GB virtual hard disk
Greenbone Enterprise EXA
12 virtual CPUs
24 GB RAM
500 GB virtual hard disk
The following hypervisors are officially supported for running a Greenbone Enterprise DECA/TERA/PETA/EXA:
Microsoft Hyper-V, version 5.0 or higher
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi), version 6.0 or higher
Huawei FusionCompute, version 8.0
For Microsoft Hyper-V, each Greenbone Enterprise CENO/DECA/TERA/PETA/EXA is delivered as a generation 2 virtual machine.
The required booting mode is the EFI/UEFI boot mode.
4.1.6 Greenbone Enterprise CENO¶
This section lists the requirements for successfully deploying a Greenbone Enterprise CENO. All requirements have to be met.
The virtual appliance requires and is limited to the following resources:
2 virtual CPUs
12 GB RAM
500 GB virtual hard disk
The following hypervisors are officially supported for running a Greenbone Enterprise CENO:
Microsoft Hyper-V, version 5.0 or higher
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi), version 6.0 or higher
For Microsoft Hyper-V, each Greenbone Enterprise CENO/DECA/TERA/PETA/EXA is delivered as a generation 2 virtual machine.
The required booting mode is the EFI/UEFI boot mode.
4.1.7 Greenbone Enterprise 25V¶
This section lists the requirements for successfully deploying a Greenbone Enterprise 25V. All requirements have to be met.
The virtual appliance requires and is limited to the following resources:
2 virtual CPUs
8 GB RAM
500 GB virtual hard disk
The following hypervisors are officially supported for running a Greenbone Enterprise 25V:
Microsoft Hyper-V, version 5.0 or higher
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi), version 6.0 or higher
Huawei FusionCompute, version 8.0
For Microsoft Hyper-V, each Greenbone Enterprise 25V is delivered as a generation 2 virtual machine.
The required booting mode is the EFI/UEFI boot mode.
4.1.8 Greenbone Basic Appliance¶
This section lists the requirements for successfully deploying a Greenbone Basic Appliance. All requirements have to be met.
The virtual appliance requires and is limited to the following resources:
2 virtual CPUs
12 GB RAM
500 GB virtual hard disk
The following hypervisors are officially supported for running a Greenbone Basic Appliance:
Microsoft Hyper-V, version 5.0 or higher
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi), version 6.0 or higher
VMware Workstation Pro, version 16.0 or higher
Oracle VirtualBox, version 6.1 or higher
Huawei FusionCompute, version 8.0
The required booting mode is the EFI/UEFI boot mode.
Note
The following steps are mandatory for a Greenbone Basic Appliance, otherwise no vulnerability scans can be performed:
Entering or uploading a Greenbone Enterprise feed subscription key (see Chapter 4.4.4)
Downloading the Greenbone Enterprise Feed (see Chapter 4.4.5)
A Greenbone Enterprise Feed subscription key should have been received with the order of the Greenbone Basic Appliance. If no key was received, contact sales@greenbone.net.
4.1.9 Greenbone Enterprise ONE¶
This section lists the requirements for successfully deploying a Greenbone Enterprise ONE. All requirements have to be met.
The virtual appliance requires and is limited to the following resources:
2 virtual CPUs
12 GB RAM
500 GB virtual hard disk
The following hypervisors are officially supported for running a Greenbone Enterprise ONE:
Oracle VirtualBox, version 6.1 or higher
VMware Workstation Pro, version 16.0 or higher
The required booting mode is the EFI/UEFI boot mode.
4.2 Setting up a Hardware Appliance¶
Note
The requirements for installing the appliance can be found in Chapter 4.1.
4.2.1 Utilizing the Serial Port¶
The enclosed console cable is used for utilizing the serial port.
To access the serial port, a terminal application is required. The application must be configured to a speed of 9600 bits/s (Baud).
Under Linux, the command screen can be used in the command line to access the serial port.
The device providing the serial port must be passed as a parameter:
screen /dev/ttyS0 #(for serial port)
screen /dev/ttyUSB0 #(for USB adapter)
Tip
After starting screen, it may be necessary to press Enter several times to see a command prompt.
To close the serial connection, press Ctrl + a and immediately afterwards \.
In Microsoft Windows, PuTTY can be used. After starting it, the options as shown in Fig. 4.1 and the appropriate serial port must be selected.
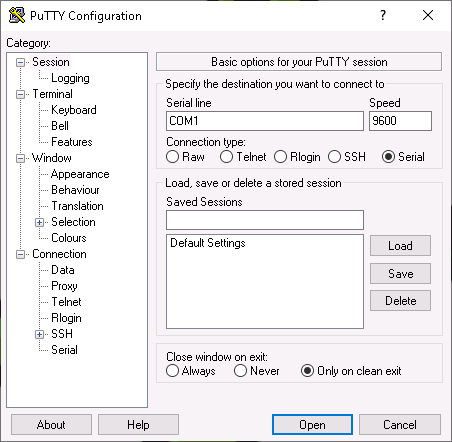
Fig. 4.1 Setting up the serial port in PuTTY¶
4.2.2 Starting the Appliance¶
Once the appliance is fully wired, a connection to the appliance using the console cable is achieved and the terminal application (PuTTY, screen or similar) is set up, the appliance can be started.
The appliance will boot and after a short time – depending on the exact model – the login prompt is shown. The default login information is:
User:
adminPassword:
admin
Note
During the first setup, this password should be changed (see Chapter 6.2.1.1).
4.3 Setting up a Virtual Appliance¶
Note
The requirements for installing the appliance can be found in Chapter 4.1.
4.3.1 Verification of Integrity¶
Note
The integrity of the virtual appliance can be verified. On request, the Greenbone Enterprise Support provides an integrity checksum.
To request the checksum, contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support including the subscription number.
The integrity checksum can be provided via phone or via support portal.
The local verification of the checksum depends on the host operating system.
On Linux systems, the following command for calculating the checksum can be used:
sha256sum <file>
Note
Replace <file> with the name of the appliance’s OVA file.
On Microsoft Windows systems, the following command for calculating the checksum can be used in the Windows PowerShell:
Get-Filehash 'C:\<path>\<file>' -Algorithm SHA256
Note
Replace <path> and <file> with the path and the name of the appliance’s OVA file.
If the checksum does not match the checksum provided by the Greenbone Enterprise Support, the virtual appliance has been modified and should not be used.
4.3.2 Deploying the Appliance¶
4.3.2.1 VMware vSphere/ESXi¶
The virtual appliance is provided by Greenbone in the Open Virtualization Appliance (OVA) format.
Each appliance is activated using a unique subscription key.
Note
Cloning the appliance and using several instances in parallel is not permitted and can result in inconsistencies and unwanted side effects.
To deploy an appliance, it has to be imported into the hypervisor of choice as follows:
Note
The example features VMware ESXi, but is also applicable for VMware vCenter.
The figures show the installation of a Greenbone Enterprise TERA. The installation of another appliance model is carried out equivalently. File names used in the example differ based on the appliance model and the subscription key.
Open the web interface of the VMware ESXi instance and log in.
Click Virtual Machines in the Navigator column on the left.
Select Deploy a virtual machine from an OVF or OVA file and click Next (see Fig. 4.2).
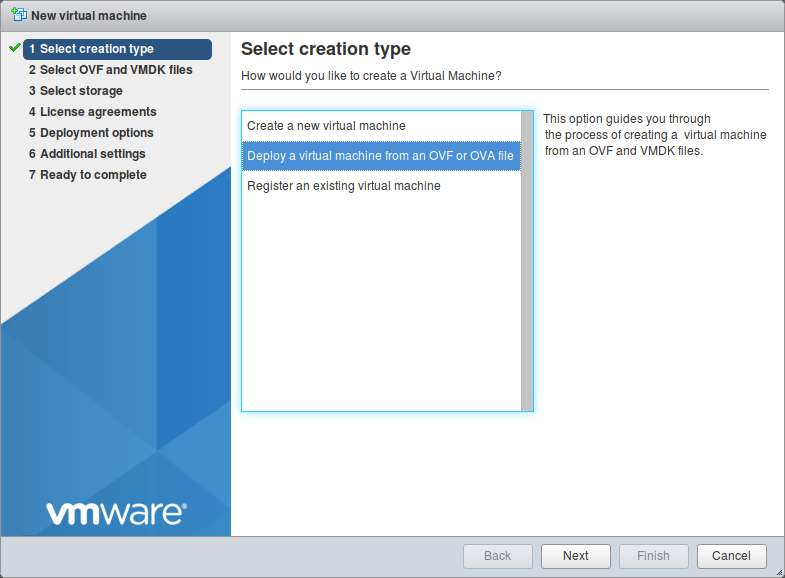
Fig. 4.2 Selecting the creation type¶
Enter a name for the virtual machine in the input box.
Click Click to select files or drag/drop, select the OVA file of the appliance and click Next.
Select the storage location in which to store the virtual machine files and click Next.
Adjust the deployment options as required and click Next.
Note
The default deployment settings may be used.
Check the configuration of the virtual machine (see Fig. 4.3).
Tip
Settings can be changed by clicking Back and adjusting them in the respective dialog.
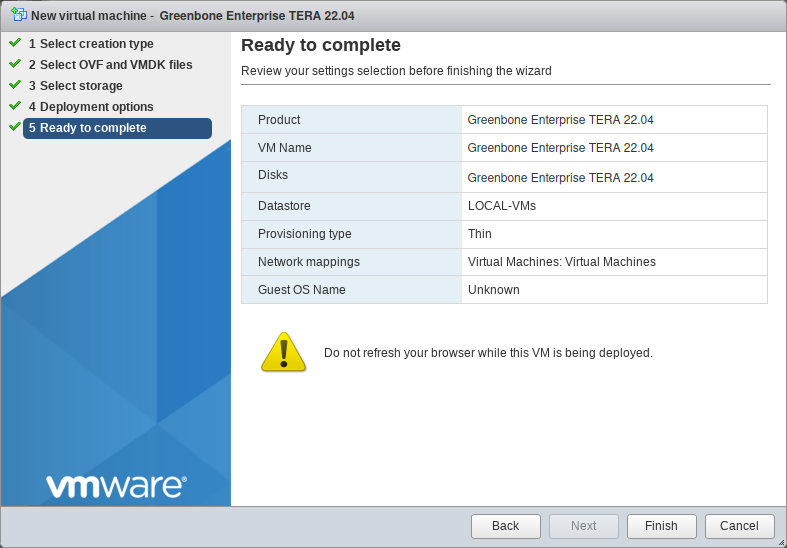
Fig. 4.3 Checking the configuration of the virtual machine¶
Click Finish.
→ The appliance is being imported. This can take up to 10 minutes.
Important
Do not refresh the browser while the virtual machine is being deployed.
When the appliance is imported, click Virtual Machines in the Navigator column on the left.
Select the appliance in the list and click
 Power on (see Fig. 4.4).
Power on (see Fig. 4.4).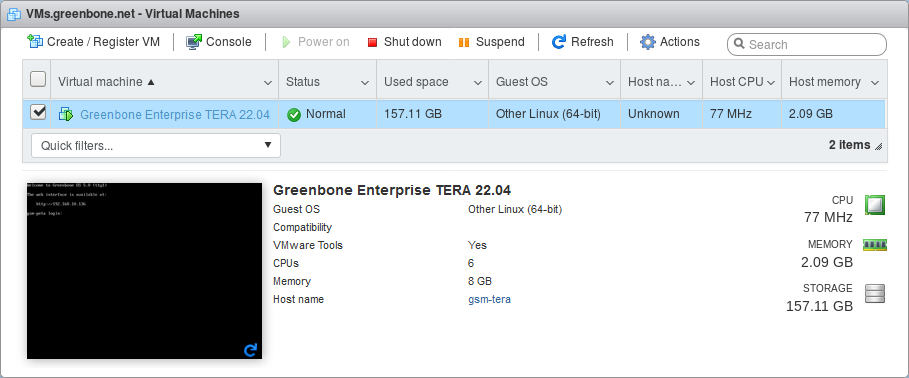
Fig. 4.4 Imported virtual machine¶
→ The appliance will boot and after a short time – depending on the exact model – the login prompt is shown.
Log in using the default login information:
User:
adminPassword:
admin
Note
During the first setup, this password should be changed (see Chapter 6.2.1.1).
4.3.2.2 Oracle VirtualBox¶
The virtual appliance is provided by Greenbone in the Open Virtualization Appliance (OVA) format.
Each appliance is activated using a unique subscription key.
Note
Cloning the appliance and using several instances in parallel is not permitted and can result in inconsistencies and unwanted side effects.
To deploy an appliance, it has to be imported into the hypervisor of choice as follows:
Note
File names used in the example differ based on the subscription key.
Install Oracle VirtualBox for the current operating system.
Note
VirtualBox is often included with Linux distributions.
Should this not be the case and or a version of Microsoft Windows is used, VirtualBox is available at https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads.
Start VirtualBox.
Select File > Import Appliance… in the menu bar.
Click
 and select the OVA file of the appliance (see Fig. 4.5).
and select the OVA file of the appliance (see Fig. 4.5).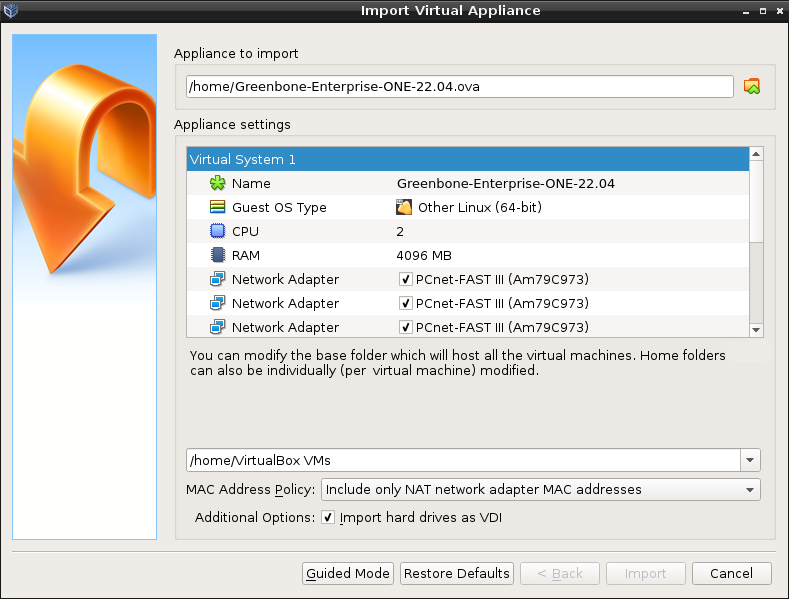
Fig. 4.5 Importing the OVA file of the appliance¶
Check the configuration of the virtual machine in the window Appliance settings (see Fig. 4.5).
Values can be changed by double clicking into the input box of the respective value.
Click Import.
→ The appliance is being imported. This can take up to 10 minutes.
When the appliance is imported, it is displayed in the left column in VirtualBox.
Select the appliance in the list and click Start.
→ The appliance will boot and after a short time – depending on the exact model – the login prompt is shown.
Log in using the default login information:
User:
adminPassword:
admin
Note
During the first setup, this password should be changed (see Chapter 6.2.1.1).
4.4 Performing a General System Setup¶
All appliances share the same way of basic configuration and readiness check.
When the appliance is delivered by Greenbone or after a factory reset, the GOS administration menu shows the first setup wizard after logging in to assist with the basic GOS configuration (see Fig. 4.6).
By selecting Yes and pressing Enter the first setup wizard is opened.
By selecting No and pressing Enter, the setup wizard is closed. Incomplete steps are displayed again when logging in the next time.
By selecting Cancel and pressing Enter, the setup wizard is closed as well. However, incomplete steps are not displayed again.
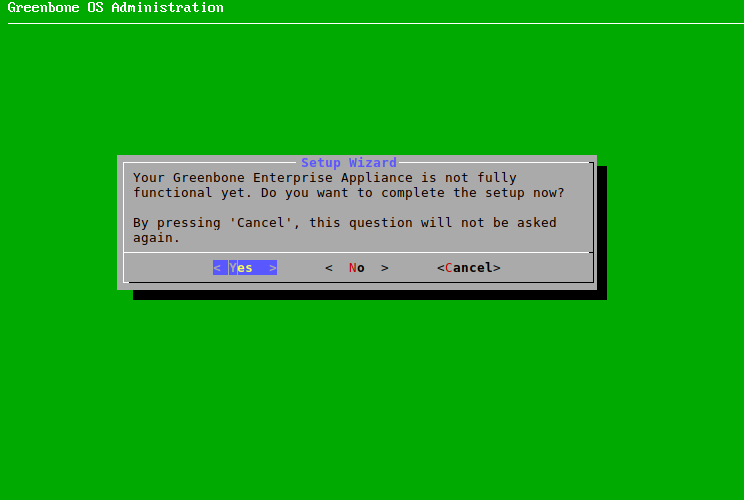
Fig. 4.6 Using the first setup wizard¶
Note
The first setup wizard is dynamic and shows only those steps necessary to operate the used appliance model. In the following, all possible steps are mentioned but they may not appear in every case.
In case of a factory reset, all steps have to be carried out (see 19.10).
Every step can be skipped by selecting Skip or No and pressing Enter. Skipped steps are displayed when logging in again.
4.4.1 Configuring the Network¶
The network must be set up for the appliance to be fully functional. If there is no IP address configured, it is asked whether the network settings should be adjusted (see Fig. 4.7).
Note
When using DHCP, the appliance does not transmit the MAC address but a DHCP Unique ID (DUID). While this should not pose a problem with modern DHCP servers, some older DHCP servers (for example Windows Server 2012) may not be able to handle it.
One possible solution is to specify the DUID instead of the MAC address on the DHCP server. Alternatively, a static IP address can be used on the appliance.
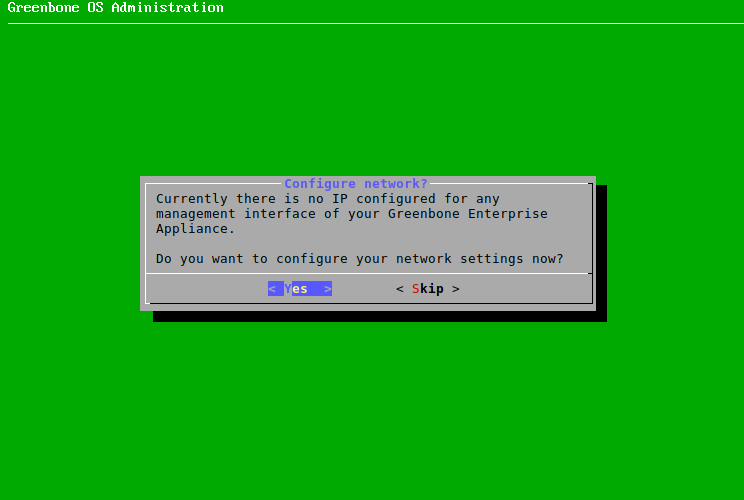
Fig. 4.7 Configuring the network settings¶
Select Yes and press Enter.
Select Interfaces and press Enter.
Select the desired interface and press Enter.
→ The interface can be configured.
If DHCP should be used, select DHCP (for IPv4 or IPv6) and press Enter (see Fig. 4.8).
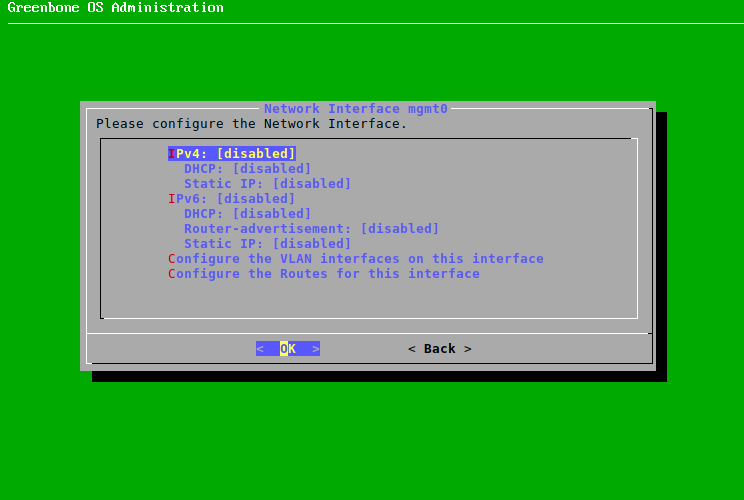
Fig. 4.8 Configuring the network interface¶
Select Save and press Enter.
Select Back and press Enter.
Select Back and press Enter.
Select Ready and press Enter.
or
If a static IP address should be used, select Static IP (for IPv4 or IPv6) and press Enter.
Enter the IP address including the prefix length in the input box (see Fig. 4.9).
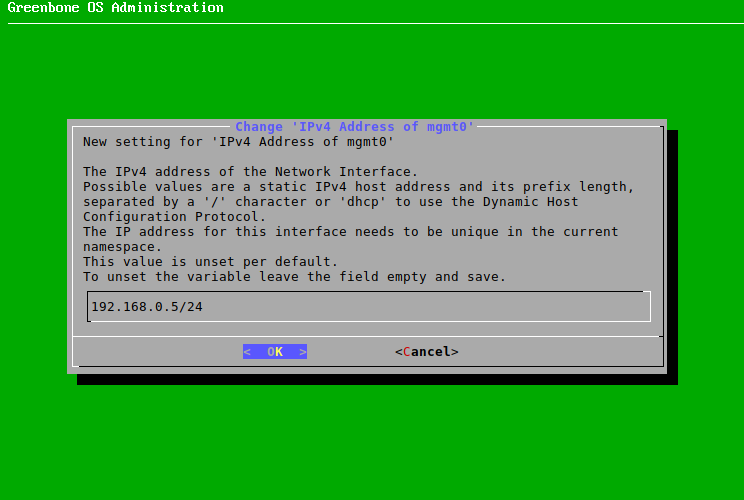
Fig. 4.9 Entering a static IP address¶
Press Enter.
→ A message informs that the changes have to be saved.
Press Enter to close the message.
Select Save and press Enter.
Select Back and press Enter.
Select Back and press Enter.
Select Ready and press Enter.
4.4.2 Importing or Generating an HTTPS Certificate¶
An HTTPS certificate must be present on the appliance to use the web interface securely. The certificate can be imported or generated as follows:
Select Import and press Enter (see Fig. 4.10).
→ A message informs that a PKCS#12 file can be imported.
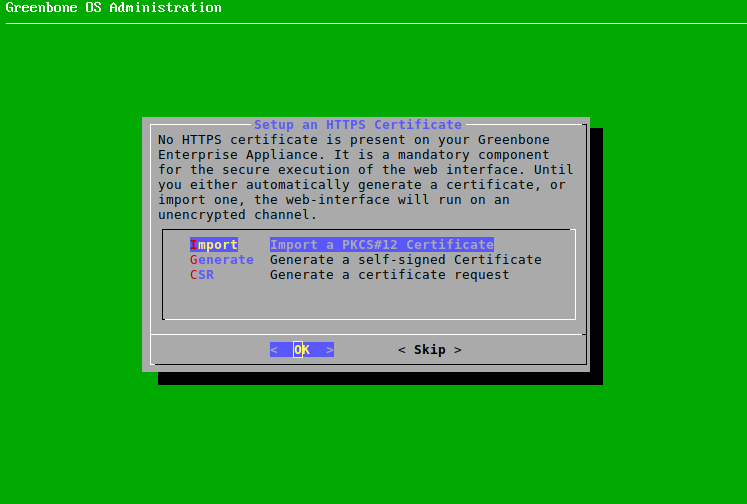
Fig. 4.10 Importing or generating an HTTPS certificate¶
Select Continue and press Enter.
Open the web browser and enter the displayed URL.
Click Browse…, select the PKCS#12 file and click Upload.
→ When the certificate is retrieved by the appliance, the GOS administration menu displays the fingerprint of the certificate for verification.
Check the fingerprint and confirm the certificate by pressing Enter.
or
Select Generate and press Enter.
→ A message informs that parameters have to be entered to generate the certificate.
Select Continue and press Enter.
Provide the settings for the certificate (see Fig. 4.11).
Note
It is valid to generate a certificate without a common name. However, a certificate should not be created without (a) Subject Alternative Name(s).
If a common name is used, it should be the same as one of the SANs.
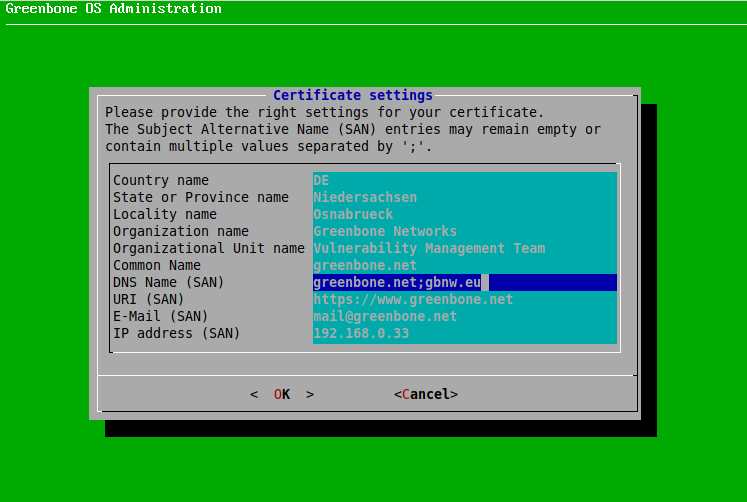
Fig. 4.11 Entering information for the certificate¶
Select OK and press Enter.
→ A message informs that the certificate is created and can be downloaded (see Fig. 4.12).
Note
The download is not done in the first setup wizard, but in the later GOS administration menu as described in Chapter 6.2.4.1.7.1, steps 1 – 4 and 9 – 13.
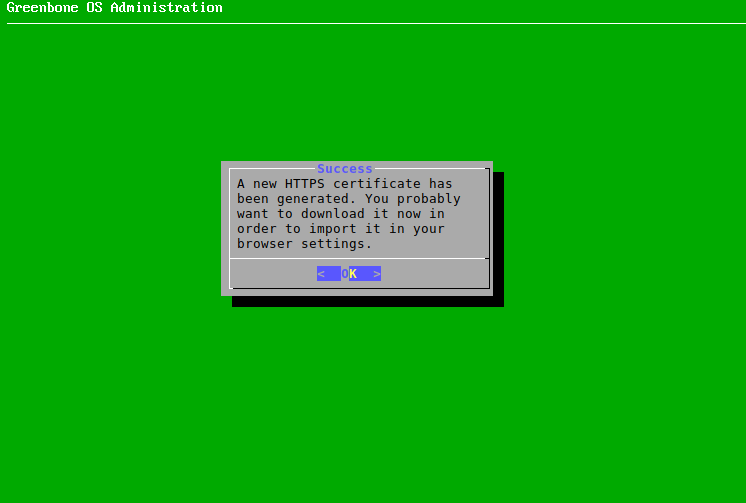
Fig. 4.12 Completing the HTTPS certificate¶
or
Select CSR and press Enter.
→ A message informs that a key pair and a certificate request are created.
Select Continue and press Enter.
Provide the settings for the certificate.
Note
It is valid to generate a certificate without a common name. However, a certificate should not be created without (a) Subject Alternative Name(s).
If a common name is used, it should be the same as one of the SANs.
Select OK and press Enter.
Open the web browser and enter the displayed URL.
Download the PEM file.
→ The GOS administration menu displays a message to verify that the CSR has not been tampered with.
Verify the information by pressing Enter.
Note
When the certificate is signed, it has to be uploaded to the appliance. The upload is not done in the first setup wizard, but in the later GOS administration menu as described in Chapter 6.2.4.1.7.2, steps 1 – 4 and 11 – 14.
4.4.3 Creating a Web Administrator¶
If there is no web administrator, it is asked whether such an account should be created (see Fig. 4.13).
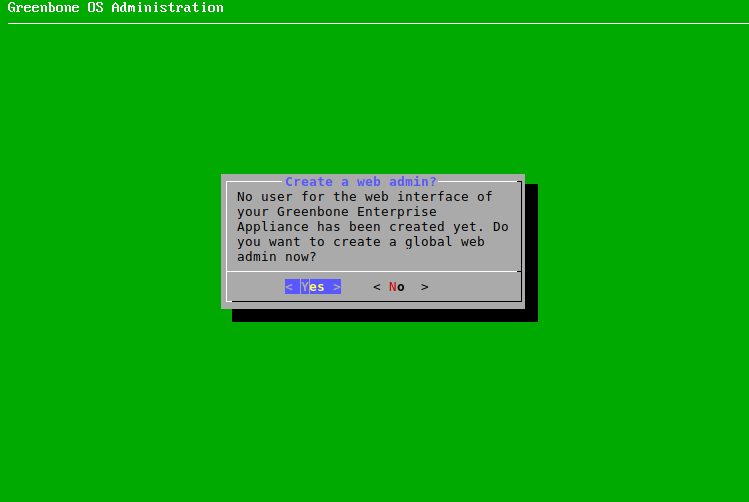
Fig. 4.13 Creating a web administrator¶
Note
A web administrator is required to use the web interface of the appliance.
The first web administrator (web user) that is created is automatically the Feed Import Owner (see Chapter 6.2.1.10).
Select Yes and press Enter.
Enter the user name for the web administrator.
Note
Only the following characters are allowed for the user name:
All alphanumeric characters
- (dash)
_ (underscore)
. (full stop)
Enter the password for the web administrator twice.
Note
The password can contain any type of character and can be at most 30 characters long.
When using special characters, note that these must be available on all used keyboards and correctly supported by all client software and operating systems. Copying and pasting special characters for passwords can lead to invalid passwords depending on these external factors.
Select OK and press Enter.
→ A message informs that the web administrator has been created.
Press Enter to close the message.
4.4.4 Entering or Uploading a Greenbone Enterprise Feed Subscription Key¶
If no valid subscription key is stored on the appliance, the appliance only uses the public Greenbone Community Feed and not the Greenbone Enterprise Feed.
Note
It is not necessary to add a Greenbone Enterprise Feed subscription key on a newly delivered appliance since a key is already pre-installed.
As an exception, the model Greenbone Basic Appliance does not come with a pre-installed subscription key and cannot be used with the Greenbone Community Feed.
A subscription key can be entered or uploaded as follows:
Select Editor and press Enter (see Fig. 4.14).
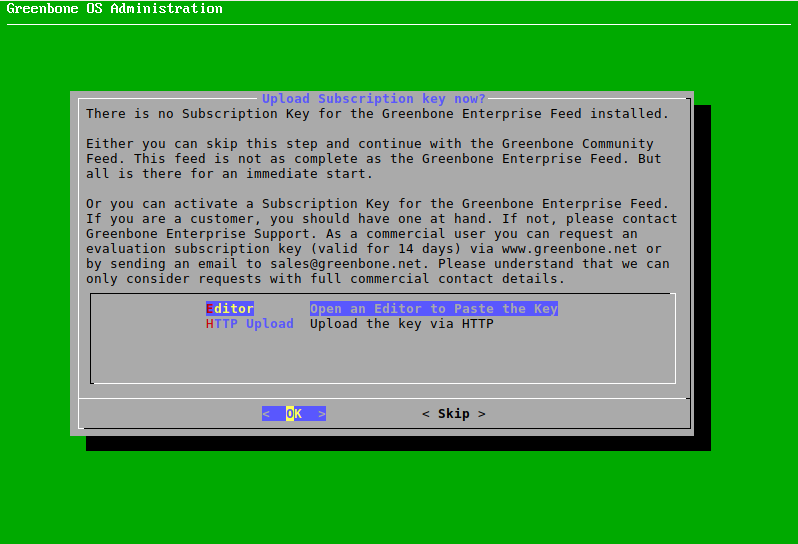
Fig. 4.14 Entering or uploading a subscription key¶
→ The editor is opened.
Enter the content of the subscription key.
Note
It is important to enter the content of the key and not the name of the key (for example
gsf2022122017).The content of the key can be displayed with any text editor or under Linux using the program
less. If the content is opened with a text editor, care must be taken to not change anything.Press Ctrl + S to save the changes.
Press Ctrl + X to close the editor.
or
Select HTTP Upload and press Enter.
Open the web browser and enter the displayed URL.
Click Browse…, select the subscription key and click Upload.
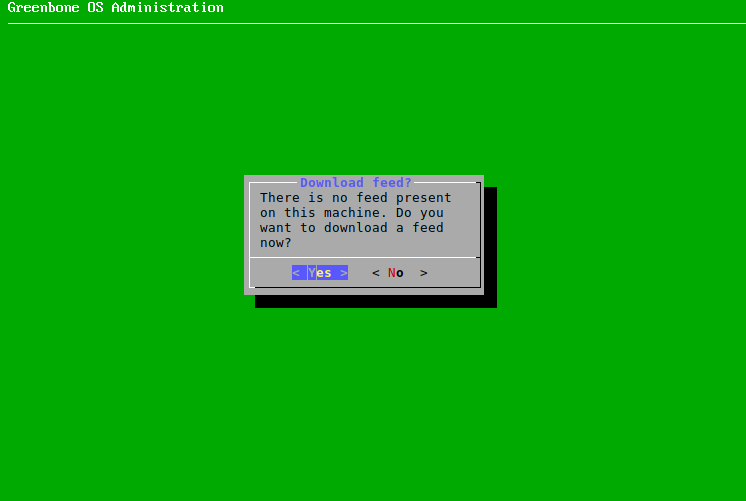
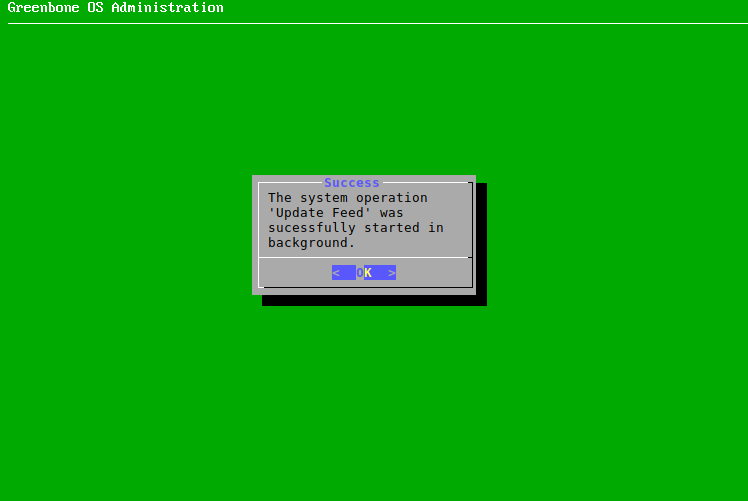
4.4.5 Downloading the Feed¶
If no feed is present on the appliance, the feed can be downloaded as follows:
4.4.6 Finishing the First Setup Wizard¶
Note
After the last step, a status check is performed.
When the check is finished, press Enter.
→ The results of the check are displayed (see Fig. 4.17).
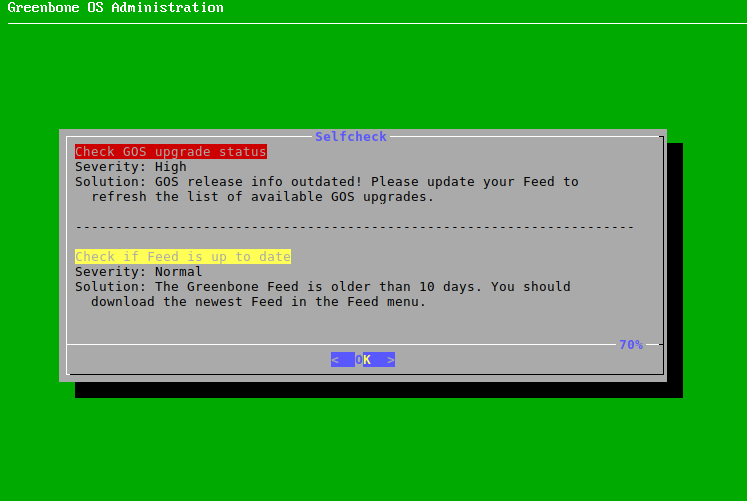
Fig. 4.17 Result of the status check¶
Press Enter.
→ The GOS administration menu can be used as described in Chapter 6.
If there are any unfinished or skipped steps, the first setup wizard is shown when logging in again.
4.5 Logging into the Web Interface¶
Note
This step does not apply for the Greenbone Enterprise 35 and the Greenbone Enterprise 25V.
The main interface of the appliance is the web interface, also called Greenbone Security Assistant (GSA). The web interface can be accessed as described in Chapter 7.1.