19 Frequently Asked Questions¶
19.1 Why Is the Scanning Process so Slow?¶
The performance of a scan depends on various aspects.
Several port scanners were activated concurrently.
If an individual scan configuration is used, select only a single port scanner in the VT family Port scanners (see Chapter 9.9.2). The VT Ping Host can still be activated.
Unused IP addresses are scanned very time-consuming.
As a first step, it is detected whether an active system is present or not for each IP address. In case it is not, this IP address will not be scanned. Firewalls and other systems can prevent a successful detection. The VT Ping Host (1.3.6.1.4.1.25623.1.0.100315) in the VT family Port scanners offers fine-tuning of the detection.
The ports to be scanned resulted in port throttling, or UDP port scanning has been chosen.
For more information, see Chapters 16.2.1.2 and 16.2.1.2.1.
19.2 What Influences the Scan Capacity?¶
The scan capacity – the scannable number of IP addresses per 24 hours – depends on the appliance model (see Chapter 3). However, the values provided for the estimated scan capacity can only be understood as guide values, as the scan capacity is influenced by many factors.
The following factors influence the scan capacity:
- Complexity of the used scan configuration
In the same amount of time, many more discovery scans can be performed than vulnerability scans. For more information about scan configurations, see Chapter 9.9.
- Using the appliance outside its specifications
Starting too many scans or scanning too many targets at once can result in performance problems.
- Performance of the network infrastructure and the target system(s)
If systems are slow to respond to network requests, the scanning process will be slower.
- Type of the scanned target system(s)
The type determines which and how many vulnerability tests are executed during a scan. More vulnerability tests usually mean slower scans.
Some scan scenarios increase resource usage, which can have an impact on performance, for example scanning of virtual hosts (vhosts) and scanning of web servers with CGI caching enabled. For more information about configuration options for those scenarios, see Chapter 9.9.
- Using the appliance in parallel while scanning
If other resource-intensive operations (for example, feed updates, generation of large reports) are running, less system resources are available for scans.
- Using sensors
Using sensors can increase the scanable IP addresses per 24 hours.
19.3 Why Is a Service/Product Not Detected?¶
The target is not detected as online/reachable.
- Solution(s):
Fix the network setup/routing to the target.
Update the criteria/test configuration to detect the target as alive (see Chapter 9.2.1).
Ensure that the scan configuration includes the following VTs from the VT family Port scanners: * Nmap (NASL wrapper) (OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.25623.1.0.14259) * Ping Host (OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.25623.1.0.100315)
Verify and remove any network device (firewall, IDS/IPS, WAF, etc.) between the scanner and the target, or any security mechanisms on the target itself. Whitelist the scanner’s IP address.
The service/product is running on a specific port not included in the port list.
- Solution(s):
Create a suitable port list (see Chapter 9.7). This is especially important for UDP ports.
There is a detection VT for an service/product available but the service/product is not found during a scan.
- Solution(s):
Fix the network setup/routing to the target.
Update the criteria/test configuration to detect the target as alive (see Chapter 9.2.1).
Verify and remove any network device (firewall, IDS/IPS, WAF, etc.) between the scanner and the target, or any security mechanisms on the target itself. Whitelist the scanner’s IP address.
Create a suitable port list (see Chapter 9.7). This is especially important for UDP ports.
If the solutions above do not help, contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support and provide more information about the service/product (product name, specific version running, etc.).
The target is not stable/responds slowly during a scan.
- Solution(s):
Lower the concurrently executed VTs (see Chapter 9.2.2).
Update the service/product to a newer version (for example to fix triggered bugs).
Assign more resources (CPU, RAM, etc.) to the target to make it more stable during scans.
19.4 Why Is a Vulnerability Not Detected?¶
The affected service/product is not detected at all.
- Solution(s):
See Chapter 19.3.
The service/product was detected but the a version extraction was not possible.
- Solution(s):
Perform an authenticated scan (see Chapter 9.3).
If the solutions above do not help, contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support and provide more information about the service/product (product name, specific version running, etc.).
There is only a version check with a lower Quality of Detection (QoD) and the vulnerability is not displayed by default.
If an authenticated scan was carried out, the login has failed.
- Solution(s):
Check the correctness of the used credentials.
Verify that the user is not blocked.
Verify that the user is allowed to log in to the target.
If the solutions above do not help, contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support and provide more information about the service/product (product name, specific version running, etc.).
The service/product itself crashed or stopped to respond during the scan.
- Solution(s):
Lower the concurrently executed VTs (see Chapter 9.2.2).
Update the service/product to a newer version (for example to fix triggered bugs).
Assign more resources (CPU, RAM, etc.) to the target to make it more stable during scans.
The vulnerability was only recently discovered and there is no VT for it yet.
- Solution(s):
Contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support and ask for a new VT or whether a VT is already planned.
The specific detection became outdated.
- Solution(s):
Contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support.
19.5 Why Do the Results for the Same Target Differ across Several Consecutive Scans?¶
The results of consecutive scans may differ due to the following reasons:
There was a loss of connection over unreliable network connections (between the scanner host and the target).
The network connection or equipment (between the scanner host and the target) was overloaded.
An overloaded target host and/or service stopped responding.
“Fragile” protocols (for example Remote Desktop Protocol) do not always respond as expected.
A previous probe/attacking request caused the service to not respond for a short period of time.
Although the scanner tries to reduce the occurrence of such situations by internal retry routines, they cannot be ruled out completely.
19.6 Why Is It Not Possible to Edit Scan Configurations, Port Lists, Compliance Policies, or Report Formats?¶
Scan configurations, port lists, compliance policies and report formats by Greenbone (hereafter referred to as “objects”) are distributed via the feed. These objects must be owned by a user, the Feed Import Owner. The objects are downloaded and updated during a feed update, if a Feed Import Owner has been set.
The objects cannot be edited. This is by design to ensure that the objects function as intended by Greenbone.
19.7 Why Is It Not Possible to Delete Scan Configurations, Port Lists, Compliance Policies, or Report Formats?¶
Scan configurations, port lists, compliance policies and report formats by Greenbone (hereafter referred to as “objects”) are distributed via the feed. These objects must be owned by a user, the Feed Import Owner. The objects are downloaded and updated during a feed update, if a Feed Import Owner has been set.
Only the Feed Import Owner, a super administrator and users who obtained respective rights are able to delete objects.
If objects are deleted, they will be downloaded again during the next feed update. If no objects should be downloaded, the Feed Import Owner must be unset.
19.8 Why Does a VNC Dialog Appear on the Scanned Target System?¶
When testing port 5900 or configuring a VNC port, a window appears on the scanned target system asking the user to allow the connection. This was observed for UltraVNC Version 1.0.2.
Solution: exclude port 5900 or other configured VNC ports from the target specification. Alternatively, upgrading to a newer version of UltraVNC would help (UltraVNC 1.0.9.6.1 only uses balloons to inform users).
19.9 Why Does the Scan Trigger Alarms on Other Security Tools?¶
For many vulnerability tests the behavior of real attacks is applied. Even though a real attack does not happen, some security tools will issue an alarm.
A known example is:
Symantec reports attacks regarding CVE-2009-3103 if the VT Microsoft Windows SMB2 ‘_Smb2ValidateProviderCallback()’ Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (1.3.6.1.4.1.25623.1.0.100283) is executed. This VT is only executed if the radio button No is selected for safe_checks in the scanner preferences (see Fig. 19.1). Otherwise the target system can be affected.
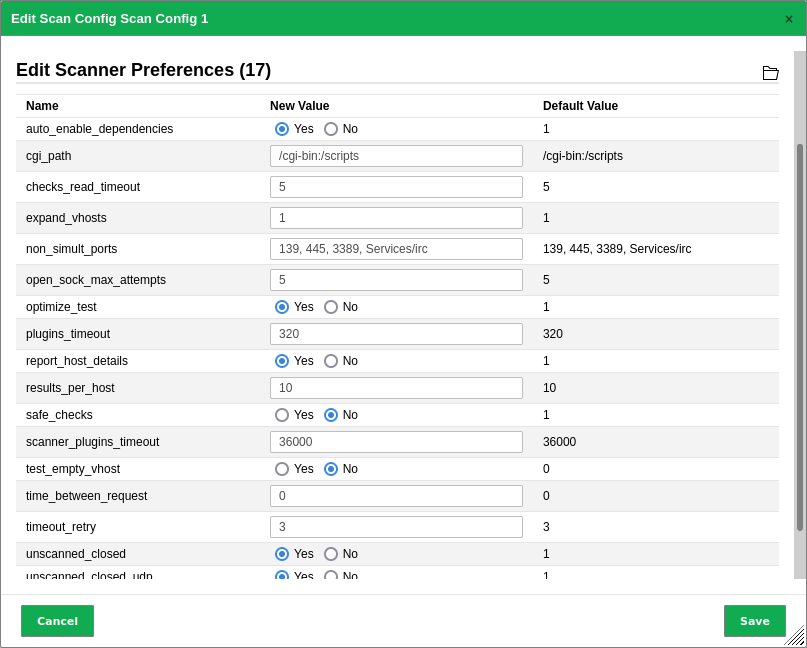
Fig. 19.1 Disabling the scanner preference safe_checks¶
19.10 How Can a Factory Reset of the Appliance Be Performed?¶
A factory reset can be performed to erase user data securely from the appliance.
Note
Contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support to receive detailed instructions on how to perform a factory reset.
19.11 Why Does Neither Feed Update nor GOS Upgrade Work After a Factory Reset?¶
A factory reset deletes the whole system including the Greenbone Enterprise Feed subscription key. The subscription key is mandatory for feed updates and GOS upgrade.
Reactivate the subscription key:
A backup key is delivered with each appliance (see Chapter 6.1.1). Use this key to reactivate the appliance. The activation is described in the setup guide of the respective appliance model (see Chapter 4).
Update the system to the current version:
Depending on the GOS version, the respective upgrade procedure has to be executed.
19.12 How Can an Older Backup or Beaming Image Be Restored?¶
Only backups and beaming images created with the currently used GOS version or the previous GOS version can be restored. For GOS 22.04, only backups and beaming images from GOS 21.04 or GOS 22.04 can be imported. If an older backup or beaming image should be imported, for example from GOS 6 or GOS 20.08, an appliance with a matching GOS version has to be used.
Backups and beaming images from GOS versions newer than the currently used GOS version are not supported as well. If a newer backup or beaming image should be imported, an appliance with a matching GOS version has to be used.
If there are any questions, contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support.
19.14 How Can the GMP Status Be Checked Without Using Credentials?¶
Build an SSH connection to the appliance via command line using the GMP user:
ssh gmp@<appliance>
Replace <appliance> with the IP address or DNS name of the appliance.
Note
No input prompt is displayed but the command can be entered nevertheless.
Enter
<get_version/>.→ If GMP is activated, the output should look like
<get_version_response status="200" status_text="OK"><version>8.0</version></get_version_response>.
19.15 What Should Be Done if the Self-Check Shows “RAID Array degraded”?¶
The appliance models Greenbone Enterprise 6500/6400/5400/5300 use RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) 6 as a software RAID. RAID is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple hard disk drive (HDD) components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy. For RAID 6, at least 4 HDDs are required for the RAID, and thus the data rendundancy, to function. The appliance itself will still function if up to 2 HDDs fail.
If one or more HDD(s) fail(s), GOS will show the self-check warnings RAID Array degraded with the hint Replace the failed disk, and Check for system integrity status with the hint The system integrity may be endangered. Please contact the support.
The integrity check fails due to the failed HDD(s).
Failed HDDs must be replaced and the RAID must be repaired. Contact the Greenbone Enterprise Support for assistance.