1 Introduction¶
1.1 Vulnerability Management¶
In IT security, the combination of three elements influence the attack surface of an IT infrastructure:
Cyber criminals with sufficient experience, equipment and money to carry out the attack.
Access to the IT infrastructure.
Vulnerabilities in IT systems, caused by errors in applications and operating systems, or incorrect configurations.
If these three elements come together, a successful attack on the IT infrastructure is likely.
Since most vulnerabilities are known and can be fixed, the attack surface can be actively influenced using vulnerability management. Vulnerability management involves looking at the IT infrastructure from the outside – just as potential cyber criminals would. The goal is to find every vulnerability that could exist in the IT infrastructure.
Vulnerability management identifies weaknesses in the IT infrastructure, assesses their risk potential, and recommends concrete measures for remediation. In this way, attacks can be prevented through targeted precautionary measures. This process – from recognition to remedy and monitoring – is carried out continuously.
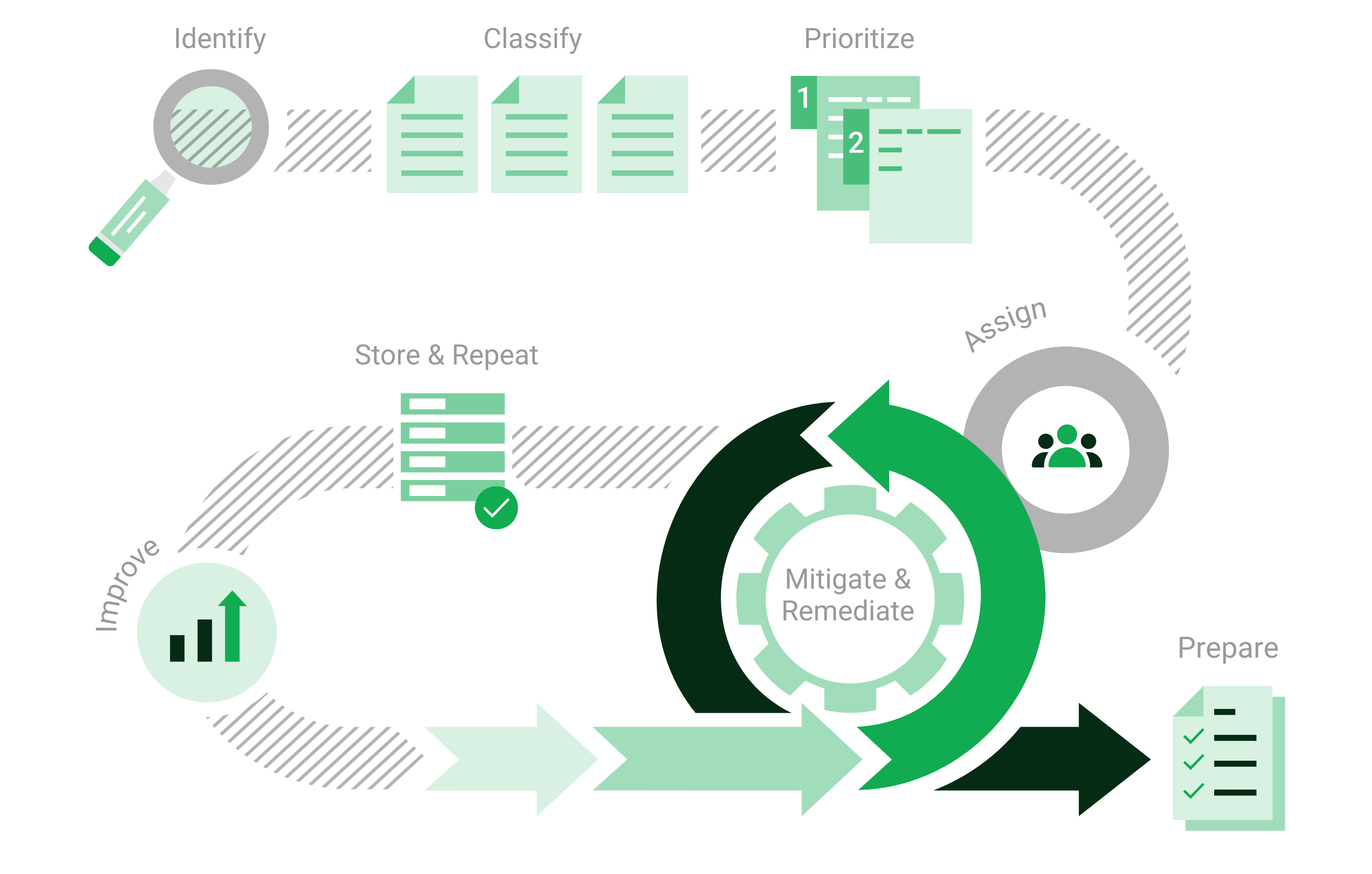
Fig. 1.1 Process of vulnerability management¶
1.2 OPENVAS REPORT¶
OPENVAS REPORT manages scan data about assets and vulnerabilities from multiple OPENVAS SCAN appliances on a unified platform. It provides an asset-centric view of all networks.
Scan data from connected appliances can be imported continuously and automatically.
With its aggregated view on scan data from several appliances, OPENVAS REPORT provides an overview of the most vulnerable assets, and the most widespread critical, high, and medium vulnerabilities. Additionally, it shows the trend of how the number of vulnerabilities has developed over time.
OPENVAS REPORT makes it possible to prioritize remediation measures for vulnerabilities. For further processing or reporting, asset and vulnerability data can be exported.