5 Upgrading OPENVAS SCAN to the Latest Major Version¶
GOS 22.04 provides seamless upgrades to the new major version GOS 24.10.
All system settings and user data are retained and automatically migrated to the new version unless a change in default behavior affects a specific setting or data. For a list of changes to the default behavior, see Chapter 5.5.
5.1 Upgrading the Operating System¶
Note
Before upgrading to GOS 24.10, some requirements must be met in GOS 22.04:
The latest version of GOS 22.04 must be installed on the appliance.
A Feed Import Owner must be set as described here.
The data objects must be installed. For this, a feed update is required after setting the Feed Import Owner.
The gnm networking mode must be set as described here.
It must be checked whether the used appliance model supports GOS 24.10. Note that the models OPENVAS SCAN 400/450/600/650 R1, OPENVAS SCAN 5300/6400 and OPENVAS SCAN 150 do not support GOS 24.10.
The upgrade to GOS 24.10 can be carried out as follows:
Select Maintenance and press Enter.
Select Upgrade and press Enter.
→ A message informs that a new GOS release is available.
Press Enter to close the message.
Select Switch Release and press Enter.
→ A warning informs that the appliance is upgraded to a major new version (see Fig. 5.1).
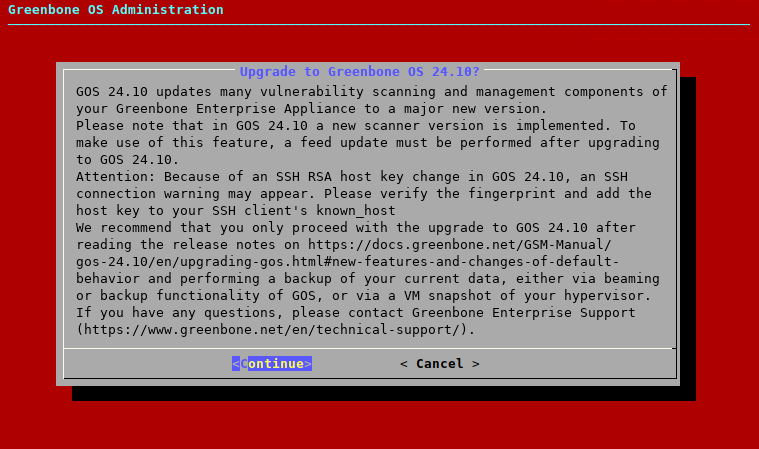
Fig. 5.1 Warning when upgrading to GOS 24.10¶
Select Continue and press Enter.
→ A warning informs that the appliance is locked during the upgrade to GOS 24.10 (see Fig. 5.2).
Note
No system operations can be run during the upgrade and all running system operations must be completed before upgrading.
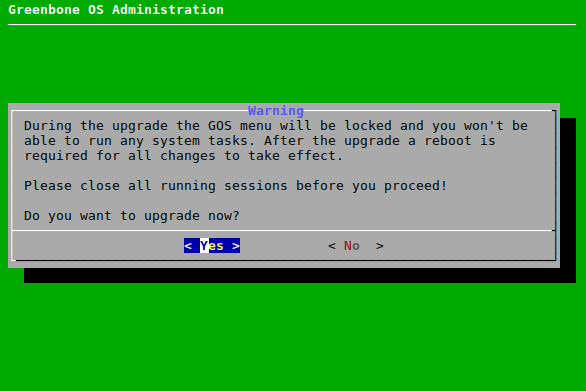
Fig. 5.2 Warning that system is locked during the upgrade¶
Select Yes and press Enter.
→ A message informs that the upgrade was started.
Note
When the upgrade is finished, a message informs that a reboot is required to apply all changes (see Fig. 5.3).
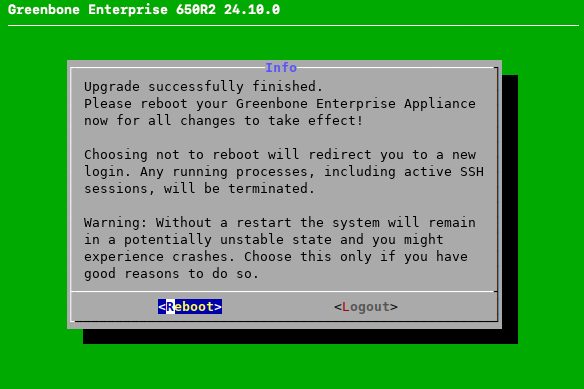
Fig. 5.3 Message after a successful upgrade¶
Select Reboot and press Enter.
→ After the reboot is finished, it is checked if there are any unfinished setup steps. If there are unfinished steps, a message asks whether they should be completed now.
Note
A feed update must be performed after upgrading to GOS 24.10 in order to make use of new features (see Chapter 5.5).
This initial feed update with GOS 24.10 will take longer and require more resources (CPU, RAM) than usual, due to the various new changes and features that are being prepared. To assure that enough system resources are available, it is recommended to wait for the feed update to finish before resuming normal usage of the appliance.
5.2 Upgrading the Flash Partition to the Latest Version¶
The internal flash partition of the appliance contains a backup copy of GOS and is used in case of a factory reset.
Upgrading the GOS version stored on the flash partition is recommended (see Chapter 6.3.8).
5.4 Reloading the Web Interface After an Upgrade¶
After an upgrade from one major version to another, the cache of the browser used for the web interface must be emptied. Clearing the browser cache can be done in the options of the used browser.
Alternatively, the page cache of every page of the web interface can be emptied by pressing Ctrl and F5.
Note
Clearing the page cache must be done for every single page.
Clearing the browser cache is global and applies to all pages.
5.5 New Features and Changes of Default Behavior¶
The following list displays the major additions and changes of default behavior between GOS 22.04 and GOS 24.10.
Depending on the currently used features, these changes may affect the currently deployed setup. For a full list of changes, see the Roadmap & Lifecycle page.
5.5.1 Product Portfolio¶
The appliance models OPENVAS SCAN 400/450/600/650 R1, OPENVAS SCAN 5300/6400 and OPENVAS SCAN 150 R1 do not support GOS 24.10.
With GOS 24.10.2, the OPENVAS SCAN 150 R1 is replaced by the OPENVAS SCAN 150 R2.
5.5.2 Secure Boot¶
GOS 24.10 supports Secure Boot for virtual appliances.
On Huawei FusionCompute, GOS 24.10 does not yet support Secure Boot.
On appliances that are shipped with GOS 24.10, Secure Boot is enabled by default, with the exception of appliances for Oracle VirtualBox.
On appliances that were upgraded from GOS 22.04 to GOS 24.10 and on new appliances for Oracle VirtualBox, Secure Boot has to be activated in the settings of the used hypervisor.
To enable Secure Boot for appliances on which it is not enabled by default, the following must be considered:
At least the hypervisor versions specified in the sub-chapters of Chapter 4.1 must be used.
The following settings must be made on the respective hypervisor:
VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi):
Guest OS Family must be set to Linux.
Guest OS Version must be set to at least Debian GNU/Linux 11 (64-bit).
VMware Workstation Pro:
Guest operating system must be set to Linux.
Guest operating system Version must be set to at least Debian GNU/Linux 11 (64-bit).
Microsoft Hyper-V:
The virtual machine must be a generation 2 virtual machine.
Secure Boot Template must be set to Microsoft UEFI Certificate Authority.
Oracle VirtualBox:
After enabling Secure Boot the first time, the Reset Keys to Default button must be pressed and the subsequent dialog must be confirmed.
To enable Secure Boot itself, refer to the technical documentation of the used hypervisor.
5.5.3 Encrypted Airgap FTP¶
GOS 24.10 introduces the option to encrypt Airgap FTP. Encryption is done via SSH-based SFTP.
When adding a server for Airgap, it is now possible to specify whether FTP or SFTP should be used. The menu options offered in the Airgap menu then depend on this selection.
5.5.4 sshd Configuration Options¶
With GOS 24.10, the algorithms and ciphers used by the SSH daemon can be configured via the GOS administration menu. The following settings are available:
Ciphers
Host key signature algorithms
Key exchange algorithms
MAC algorithms
Public key signature algorithms
5.5.5 Networking Mode¶
The old networking mode that was superseded by the networking mode gnm (GOS Network Manager) with GOS 21.04 has been removed. Upgrading from GOS 22.04 to GOS 24.10 is not possible if the old networking mode is still in use with GOS 22.04.
5.5.6 Superuser Password¶
With GOS 24.10, the method of setting the superuser password is changed. It is also no longer restored when restoring a beaming image or a backup, but remains unchanged from its previous value before the import or restore.
The superuser password can be changed as described in Chapter 6.4.2.1.
5.5.7 New openssh and libssh Versions¶
With GOS 24.10, the included packages openssh and libssh are upgraded.
openssh: version 9.2 is used as opposed to version 8.4 in the previous GOS version. This may affect the interoperability with legacy systems using old SSH implementations. False-positive vulnerabilities with a low quality of detection may be found when scanning an appliance itself.
libssh: version 1.10 is used as opposed to version 1.9 in the previous GOS version. This may affect the interoperability with scan targets using old SSH implementations.
5.5.8 Web Interface¶
5.5.8.1 New Design of the Web Interface¶
GOS 24.10 introduces a new design for the web interface. The main navigation bar has been moved to a vertical menu on the left side of the screen, and the layout and color of all pages and dialogs has been improved to enhance clarity and usability. In addition, several new functionalities have been added (see below).
With GOS 24.10.2, dynamic notifications are added to the web interface. For various types of actions, such as starting, stopping or resuming a scan task or audit, or deleting, cloning or exporting any object, a message appears in the upper right corner.
5.5.8.2 Configurable Report Formats¶
GOS 24.10 adds the feature Report Configs to customize report formats. The following report formats can be customized:
Customizable CSV Results: customization of included columns and formula handling
Topology SVG: customization of graph type and node distance
Verinice ISM: customization of attached report formats and the sent message
Verinice ISM all results: customization of attached report formats and the sent message
For the supported report formats, the report configuration can be selected when exporting a report or using an alert that includes the sending of a report.
5.5.8.3 EPSS Support¶
With GOS 24.10, EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System) scores are added to CVEs and vulnerability tests. EPSS is a measure of a vulnerability’s likelihood of exploitation.
CVEs and VTs are now assigned a score and a percentile. The score indicates the probability of attempts to exploit a vulnerability being observed in the next 30 days and is a number between 0 and 1. The higher the value, the greater the probability that a vulnerability will actually be exploited. The percentile indicates the proportion of vulnerabilities that were rated the same or lower than the vulnerability. This helps putting the score into context.
5.5.8.4 CVSS v4.0 Support¶
With GOS 24.10, CVSS v4.0 will be supported. However, since CVSS v4.0 is still in the early stages of industry-wide adoption, CVSS v4.0 data is not yet available in the feed.
5.5.8.5 Dedicated Page for Audit Reports¶
GOS 24.10 adds a new sub-page to the Resilience menu of the web interface: Compliance Audit Reports.
This page contains the reports of compliance audits, equivalent to the Reports page, which contains the reports for scan tasks. The table on the page displays an overall compliance assessment of the target system, as well as the number of results per compliance level Yes, No and Incomplete.
The details view of a report is also equivalent to that of a scan task. It contains all detected results together with an assessment of whether the requirement has been met, not met or only partially met.
Filters and tags were adjusted and are not separate between audit and scan reports. Additionally, tag types for compliance policies and audits were added.
5.5.8.6 Kerberos Credentials¶
With GOS 24.10.2, a new credential type for Kerberos authentication on Microsoft Windows systems is added. Authenticated scans via Kerberos will still be done with the help of the SMB protocol.
The already existing SMB credentials, which use NT (New Technology) LAN Manager (NTLM) for authentication, are renamed to SMB (NTLM) on the web interface to avoid confusion. If the authentication via Kerberos fails, NTLM authentication will be tried as a fallback.
In order to be able to authenticate via Kerberos on a scan target, the appliance must use a DNS server that is capable of doing a reverse lookup of the target. If the scan is performed using a sensor appliance, the sensor appliance must also fulfill this requirement. On the target side, it is also required that the system is part of a functioning Microsoft Windows domain with a working domain controller, DNS infrastructure, and network.
5.5.9 Notus scanner replaced by openvasd¶
With GOS 24.10, the Notus Scanner is replaced by openvasd. Implemented in the Rust programming language, openvasd offers a more secure and robust experience. It is the first step towards implementing all OpenVAS scanner functionalities in Rust in the future.
The local security check (LSC) functionality itself is now handled via the /notus endpoint of openvasd.
In order to speed up LSCs, the OpenVAS scanner sends the collected packages to openvasd.
The transmission is done via HTTP and the openvasd listener is bound to localhost.
5.5.10 Greenbone Management Protocol (GMP)¶
The Greenbone Management Protocol (GMP) has been updated to version 22.7 and the API has been adjusted slightly. The usage of some commands has changed and several commands, elements and attributes have been deprecated. The complete reference guide and the list of changes are available here.
If gvm-tools and/or python-gvm are to be used with GMP 22.7 and GOS 24.10, the following versions are required:
gvm-tools: 25.1.1 or higher
python-gvm: 26.0.0 or higher