1 Introduction¶
1.1 Vulnerability Management¶
In IT security, the combination of three elements influence the attack surface of an IT infrastructure:
Cyber criminals with sufficient experience, equipment and money to carry out the attack.
Access to the IT infrastructure.
Vulnerabilities in IT systems, caused by errors in applications and operating systems, or incorrect configurations.
If these three elements come together, a successful attack on the IT infrastructure is likely.
Since most vulnerabilities are known and can be fixed, the attack surface can be actively influenced using vulnerability management. Vulnerability management involves looking at the IT infrastructure from the outside – just as potential cyber criminals would. The goal is to find every vulnerability that could exist in the IT infrastructure.
Vulnerability management identifies weaknesses in the IT infrastructure, assesses their risk potential, and recommends concrete measures for remediation. In this way, attacks can be prevented through targeted precautionary measures. This process – from recognition to remedy and monitoring – is carried out continuously.
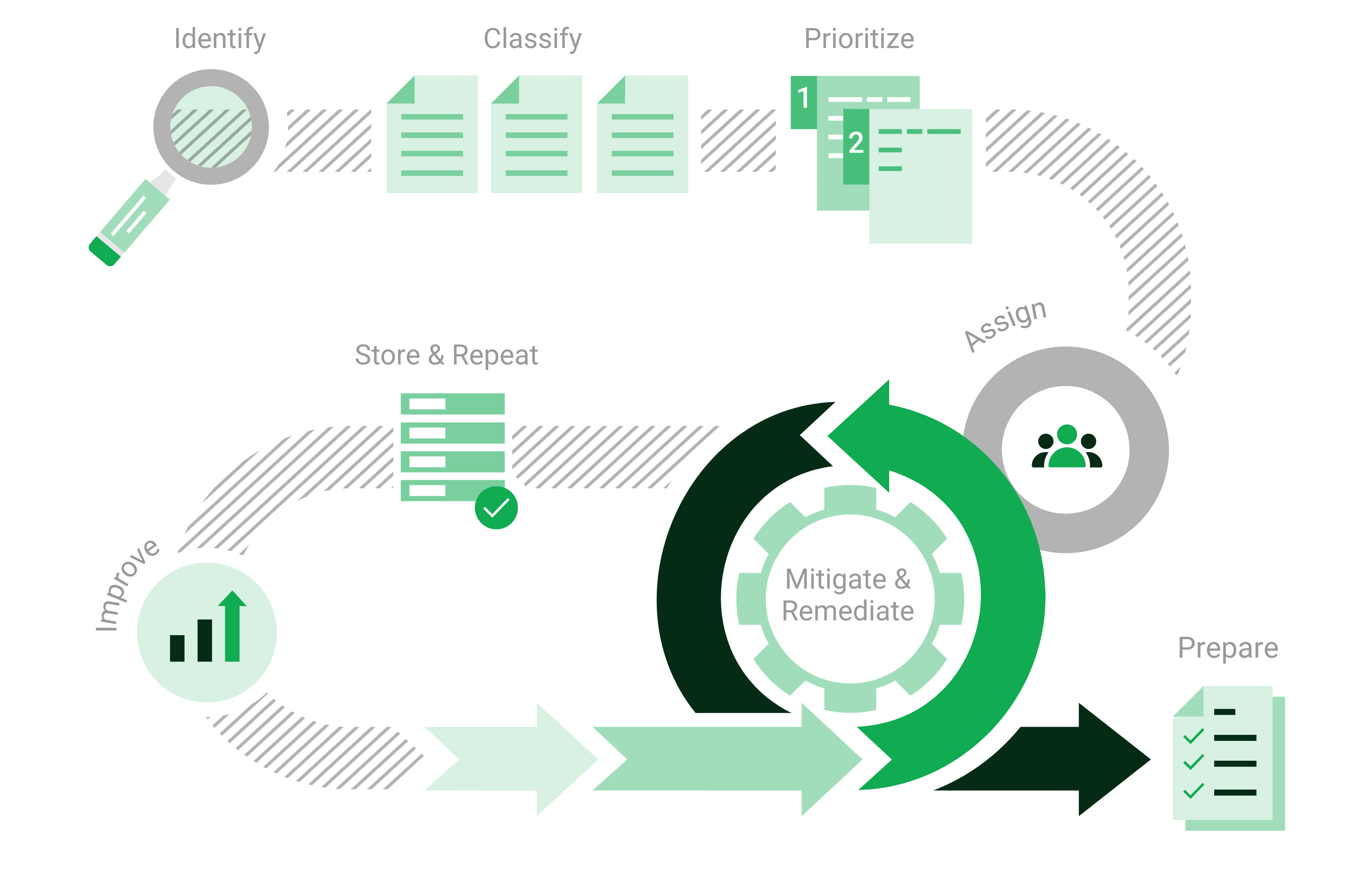
Fig. 1.1 Process of vulnerability management¶
1.2 Greenbone Cloud Service¶
The Greenbone Cloud Service offers an easy-to-use high-quality service for vulnerability management. It checks the IT infrastructure for security gaps and delivers a report containing all found vulnerabilities, sorted by severity.
For this purpose, the Greenbone Cloud Service offers the possibility to individually define the number of IP addresses to be scanned. Commercial and public entities of any size can use the Greenbone Cloud Service in self-service to address their specific security needs.
Users log in using their access data and are able to work with the Greenbone Cloud Service independent of their location. While doing so, both public IP services (WWW server, e-mail server, etc.) and internal networks can be scanned. The packages are structured as subscriptions and can be terminated or edited on a monthly basis.
The Greenbone Cloud Service discovers vulnerabilities through different perspectives of an attacker:
- External
The Greenbone Cloud Service can simulate an external attack to identify outdated or misconfigured firewalls.
- Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
The Greenbone Cloud Service can identify actual vulnerabilities that may be exploited by attackers that get past the firewall.
- Internal
The Greenbone Cloud Service can also identify exploitable vulnerabilities in the internal network, for example those targeted by social engineering or computer worms. Due to the potential impact of such attacks, this perspective is particularly important for the security of any IT infrastructure.
- Information about web application scanning
The vulnerability scanner of the Greenbone Cloud Service scans hosts, specified by a domain name or an IP address. A website URL, however, consists of more parts than just a domain name or an IP address. Since the scanner does not process the other parts of a URL, it cannot automatically analyze and test the structure of a website. It is therefore not a Web Application Security Scanner (WASS) or an HTTP scanner.
However, if a host is scanned on which a web application is running, and if both a known vulnerability exists and a suitable vulnerability test for it is included in the feed, the Greenbone Cloud Service may still detect the vulnerability.
For DMZ and internal scans, a distinction can be made between authenticated and unauthenticated scans. When performing an authenticated scan, the Greenbone Cloud Service uses credentials and can discover vulnerabilities in applications that are not running as a service but have a high risk potential. This includes web browsers, office applications or PDF viewers. For the advantages and disadvantages of authenticated scans see Chapter 5.3.1.
Due to new vulnerabilities being discovered on a daily basis, regular updates and testing of systems are required. The OPENVAS ENTERPRISE FEED ensures that the Greenbone Cloud Service is provided with the latest testing routines and can discover the latest vulnerabilities reliably. Greenbone analyzes CVE [1] messages and security bulletins of vendors and develops new vulnerability tests daily.
When performing a vulnerability scan using the Greenbone Cloud Service, the personnel responsible will receive a list of vulnerabilities that have been identified in the target systems. For the selection of remediation measures a prioritization is required. The most important measures are those that protect the system against critical risks and eliminate the corresponding security holes.
The Greenbone Cloud Service utilizes the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). CVSS is an industry standard for the classification and rating of vulnerabilities. It assists in prioritizing the remediation measures.
Fundamentally, there are two options to deal with vulnerabilities:
Eliminating the vulnerability by updating the software, removing the component or changing the configuration.
Implementing a rule in a firewall or a intrusion prevention system (virtual patching).
Virtual patching is the apparent elimination of the vulnerability through a compensating control. The real vulnerability still exists and the attacker can still exploit the vulnerability if the compensating control fails or if an alternate approach is used.
An actual patch or update of the affected software is always preferred over virtual patching.
The Greenbone Cloud Service also supports the testing of the implemented remediation measures. With its help responsible personnel can document the current state of IT security, recognize changes and record these changes in reports.
Footnotes