20 Frequently Asked Questions¶
20.1 Why is the Scanning Process so Slow?¶
The performance of a scan depends on various aspects.
Several port scanners were activated concurrently.
If an individual scan configuration is used, select only a single port scanner in the VT family Port scanners (see Chapter 10.9.2). The VT Ping Host can still be activated.
Unused IP addresses are scanned very time-consuming.
As a first step, it is detected whether an active system is present or not for each IP address. In case it is not, this IP address will not be scanned. Firewalls and other systems can prevent a successful detection. The VT Ping Host (1.3.6.1.4.1.25623.1.0.100315) in the VT family Port scanners offers fine-tuning of the detection.
20.2 Why Is a Service/Product Not Detected?¶
The target is not detected as online/reachable.
- Solution(s):
- Fix the network setup/routing to the target.
- Update the criteria/test configuration to detect the target as alive (see Chapter 10.2.1).
- Verify and remove any network device (firewall, IDS/IPS, WAF, etc.) between the scanner and the target, or any security mechanisms on the target itself. Whitelist the scanner’s IP address.
The service/product is running on a specific port not included in the port list.
- Solution(s):
- Create a suitable port list (see Chapter 10.7). This is especially important for UDP ports.
There is a detection VT for an service/product available but the service/product is not found during a scan.
- Solution(s):
- Fix the network setup/routing to the target.
- Update the criteria/test configuration to detect the target as alive (see Chapter 10.2.1).
- Verify and remove any network device (firewall, IDS/IPS, WAF, etc.) between the scanner and the target, or any security mechanisms on the target itself. Whitelist the scanner’s IP address.
- Create a suitable port list (see Chapter 10.7). This is especially important for UDP ports.
- If the solutions above do not help, contact the Greenbone Networks Support (support@greenbone.net) and provide more information about the service/product (product name, specific version running, etc.).
The target is not stable/responds slowly during a scan.
- Solution(s):
- Lower the concurrently executed VTs (see Chapter 10.2.2).
- Update the service/product to a newer version (e.g., to fix triggered bugs).
- Assign more resources (CPU, RAM, etc.) to the target to make it more stable during scans.
20.3 Why Is a Vulnerability Not Detected?¶
The affected service/product is not detected at all.
- Solution(s):
- See Chapter 20.2.
The service/product was detected but the a version extraction was not possible.
- Solution(s):
- Perform an authenticated scan (see Chapter 10.3).
- If the solutions above do not help, contact the Greenbone Networks Support (support@greenbone.net) and provide more information about the service/product (product name, specific version running, etc.).
There is only a version check with a lower Quality of Detection (QoD) and the vulnerability is not displayed by default.
If an authenticated scan was carried out, the login has failed.
- Solution(s):
- Check the correctness of the used credentials.
- Verify that the user is not blocked.
- Verify that the user is allowed to log in to the target.
- If the solutions above do not help, contact the Greenbone Networks Support (support@greenbone.net) and provide more information about the service/product (product name, specific version running, etc.).
The service/product itself crashed or stopped to respond during the scan.
- Solution(s):
- Lower the concurrently executed VTs (see Chapter 10.2.2).
- Update the service/product to a newer version (e.g., to fix triggered bugs).
- Assign more resources (CPU, RAM, etc.) to the target to make it more stable during scans.
The vulnerability was only recently discovered and there is no VT for it yet.
- Solution(s):
- Contact the Greenbone Networks Support (support@greenbone.net) and ask for a new VT or whether a VT is already planned.
The specific detection became outdated.
- Solution(s):
- Contact the Greenbone Networks Support (support@greenbone.net).
20.4 Why Is It Not Possible to Edit Scan Configurations/Port Lists/Compliance Policies/Report Formats?¶
Scan configurations, port lists, compliance policies and report formats by Greenbone Networks (hereafter referred to as “objects”) are distributed via the feed. These objects must be owned by a user, the Feed Import Owner. The objects are downloaded and updated during a feed update, if a Feed Import Owner has been set.
The objects cannot be edited. This is by design to ensure that the objects function as intended by Greenbone Networks.
20.5 Why Is It Not Possible to Delete Scan Configurations/Port Lists/Compliance Policies/Report Formats?¶
Scan configurations, port lists, compliance policies and report formats by Greenbone Networks (hereafter referred to as “objects”) are distributed via the feed. These objects must be owned by a user, the Feed Import Owner. The objects are downloaded and updated during a feed update, if a Feed Import Owner has been set.
Only the Feed Import Owner, a super administrator and users who obtained respective rights are able to delete objects.
If objects are deleted, they will be downloaded again during the next feed update. If no objects should be downloaded, the Feed Import Owner must be unset.
20.6 Why Are Less Scan Configurations/Port Lists/Compliance Policies/Report Formats Visible Than With Previous GOS Versions?¶
Scan configurations, port lists, compliance policies and report formats by Greenbone Networks (hereafter referred to as “objects”) are distributed via the feed. These objects must be owned by a user, the Feed Import Owner. The objects are downloaded and updated during a feed update, if a Feed Import Owner has been set.
By default, only the roles User, Admin and Super Admin have read access to the objects, i.e., they can see and use them on the web interface.
However, the roles that should have read access to the objects can be selected as described in Chapter 7.2.1.9.2.
Additionally, the number of objects included in the Greenbone Community Feed (GCF) was reduced. If the GCF is used, less objects will be visible with GOS 20.08 in comparison to previous GOS versions.
20.7 Why Does a VNC Dialog Appear on the Scanned Target System?¶
When testing port 5900 or configuring a VNC port, a window appears on the scanned target system asking the user to allow the connection. This was observed for UltraVNC Version 1.0.2.
Solution: exclude port 5900 or other configured VNC ports from the target specification. Alternatively, upgrading to a newer version of UltraVNC would help (UltraVNC 1.0.9.6.1 only uses balloons to inform users).
20.8 Why Does the Scan Trigger Alarms on Other Security Tools?¶
For many vulnerability tests the behaviour of real attacks is applied. Even though a real attack does not happen, some security tools will issue an alarm.
A known example is:
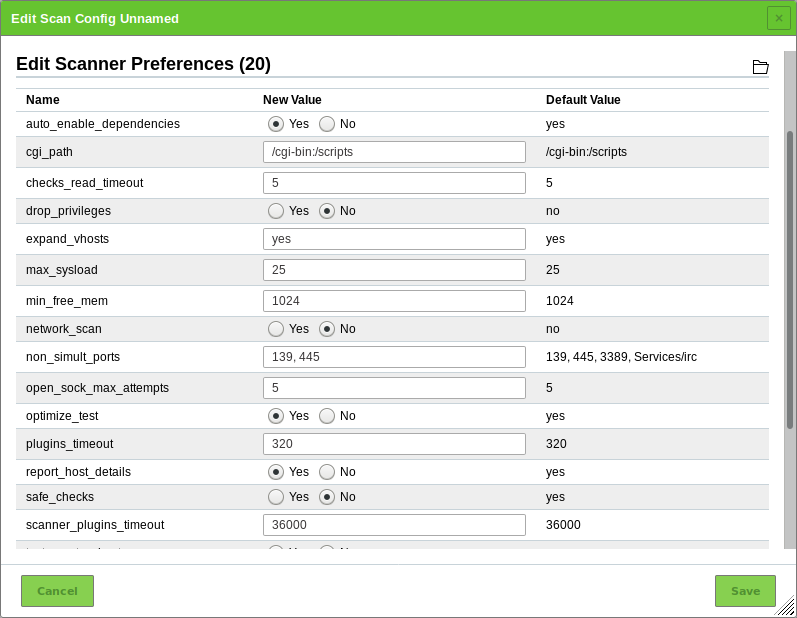
Symantec reports attacks regarding CVE-2009-3103 if the VT Microsoft Windows SMB2 ‘_Smb2ValidateProviderCallback()’ Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (1.3.6.1.4.1.25623.1.0.100283) is executed. This VT is only executed if the radio button No is selected for safe_checks in the scanner preferences (see Fig. 20.1). Otherwise the target system can be affected.
20.9 How Can a Factory Reset of the GSM Be Performed?¶
A factory reset can be performed to erase user data securely from the GSM.
Note
Contact the Greenbone Networks Support via e-mail (support@greenbone.net) to receive detailed instructions on how to perform a factory reset.
20.10 Why Does Neither Feed Update nor GOS Upgrade Work After a Factory Reset?¶
A factory reset deletes the whole system including the Greenbone Security Feed (GSF) subscription key. The GSF subscription key is mandatory for feed updates and GOS upgrade.
Reactivate the GSF subscription key:
A backup key is delivered with each GSM appliance (see Chapter 7.1.1). Use this key to reactivate the GSM. The activation is described in the setup guide of the respective GSM model (see Chapter 5).
Update the system to the current version:
Depending on the GOS version, the respective upgrade procedure has to be executed.
20.11 How Can an Older Backup Be Restored?¶
Only backups created with the currently used GOS version or the previous GOS version can be restored. For GOS 20.08, only backups from GOS 6 or GOS 20.08 can be imported. If an older backup should be imported, e.g., from GOS 4 or GOS 5, an appliance with a matching GOS version has to be used.
Backups from GOS versions newer than the currently used GOS version are not supported as well. If a newer backup should be imported, an appliance with a matching GOS version has to be used.
If there are any questions, contact the Greenbone Networks Support via e-mail (support@greenbone.net).
20.13 How Can the GMP Status Be Checked Without Using Credentials?¶
Build an SSH connection to the GSM via command line using the GMP user:
ssh gmp@<gsm>
Replace <gsm> with the IP address or DNS name of the GSM appliance.
Note
No input prompt is displayed but the command can be entered nevertheless.
Enter
<get_version/>.→ If GMP is activated, the output should look like
<get_version_response status="200" status_text="OK"><version>8.0</version></get_version_response>.